Detail
DetailPHOIBOS 100 MCD5 (inkl. PHOIBOS 100-63 MCD)
High-performance Hemipsherical Energy Analyzer with MCD Detector for UPS, XPS, ISS and LEISS.
The PHOIBOS 100 Hemispherical Energy Analyzer is a powerful tool for modern photoelectron spectroscopy. This analyzer can be operated in all relevant analysis modes, such as XPS, UPS, as well as AES, ISS and LEISS. Its design and the modular supplementary hardware makes this analyzer the most versatile PES analyzer in the market. It can easily be upgraded with all available SPECS detection systems.
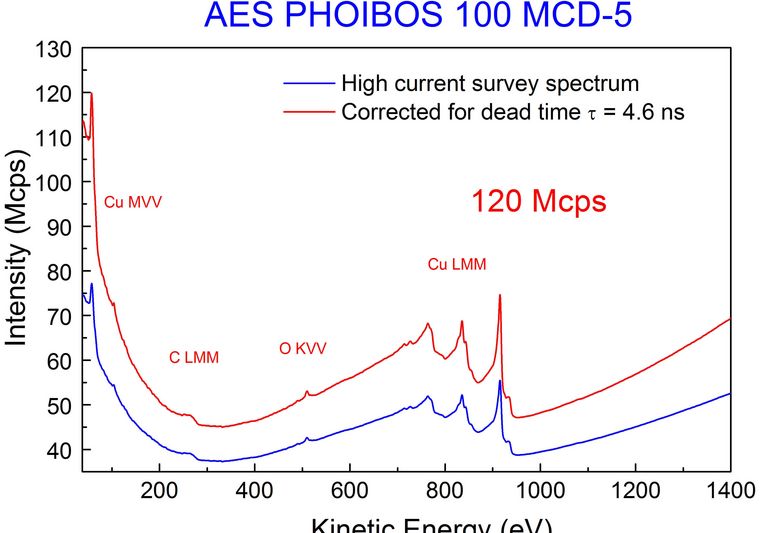
The integrated MCD-5 (5 channel multi channeltron detector) detector is a well established and robust detection solution. The direct detection of electron signals yield quantitative counts per second (cps). With 5 simultaneous channels aquisition with high count rates can be guaranteed.
The energy analyzer section is equipped with 8 customizable entrance and 3 exit slits for UPS and XPS. The analyzer comes with a highly stable power supply, the HSA 3500 plus, for best performance in a wide kinetic energy range up to 3500 eV.
A special version with a smaller lens diamater (DN63CF) is available on request.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Energy Dispersion by | Hemisphere |
| Slits/Apertures | 8 Entrance, 3 Exit slits and Iris aperture |
| Lens Modes | |
| Electronics | HSA 3500 plus HT 100 |
| Working Pressure | 10-11 to 10-7 mbar |
| Acceptance Angle | ±15° |
| Measurement Modes | |
| Energy Window | 20% of Pass Energy |
| Kinetic Energy Range | 0 - 3500 eV |
| Pass Energies | 0 - 550 eV continously adjustable |
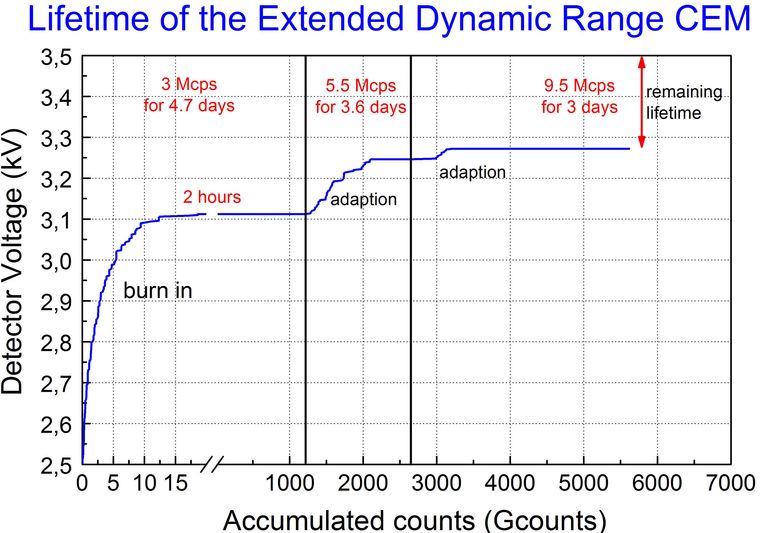
| Detector | MCD 5 |
| Detector Channels | 5 |
| Angular Resolution | < 0.5° |
| Energy Resolution | <10 meV for XPS |
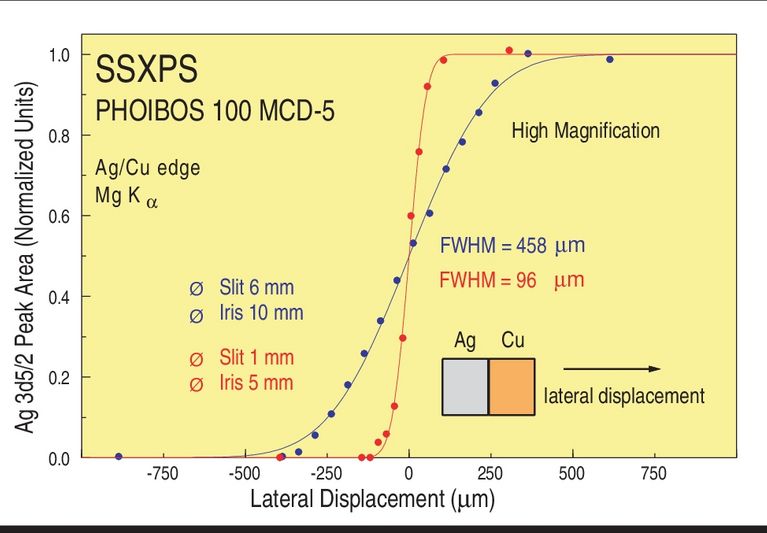
| Lateral Resolution | < 100 µm |
| XPS Count Rates UHV | Ag 3d measured with XR 50 300 W MgKa > 1.7 Mcps @ 0.85 eV, > 4.6 Mcps @ 1.00 eV |
| Magnetic Shielding | Double µ-Metal Shielding |
| Mounting Flange | DN100 CF |
| Electric Isolation | up to 7 keV |
| Working Distance | 40 mm |
SPARE PARTS

Refurbished and tested MCD-5 detector for PHOIBOS 100

Replacement for 5-channel channelron detector MCD-5 for PHOIBOS 100
PHOIBOS 100 analyzer main flange gasket for Releases R3, R6, R7

Replacement feedthrough for PHOIBOS Release R5 & R6 iris mechanism

Replacement spindle for PHOIBOS Release R5 & R6 iris mechanism