Detail
DetailTHEMIS 1000 2D-DLD
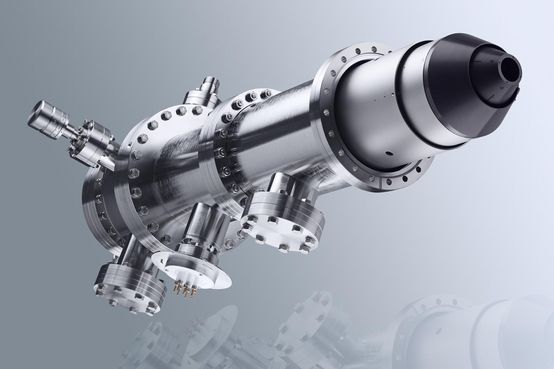
Time-of-Flight Electron Energy Analyzer for ARPES and 2D DLD Detector and 1000 mm Drift Tube
The SPECS THEMIS is a time-of-flight analyzer, ideally suited for pulsed light sources with high repetition rates. The electron dispersion is done by the different travel time through the drift tube, when a bunch of electrons is emitted from a short laser pulse. Depending on the kinetic energy window, an ultra high resolution in the sub-meV range can be detected.
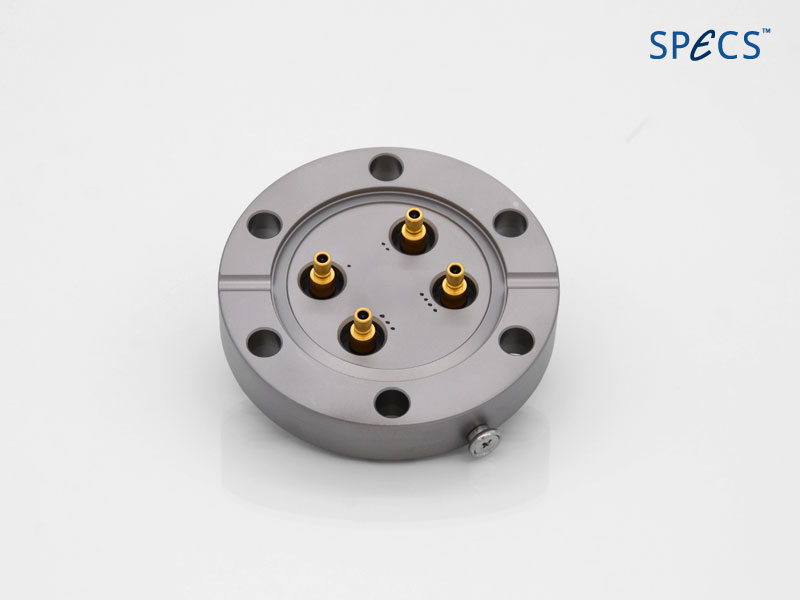
The detection system is the 2D DLD detector with x and y detection for angular resolved data and integrated 240 ps time resolution. The native repetition rate is 5-8 MHz and an optional frequency extension to 50-80 MHz is available.
The THEMIS 1000 comes with a 1000 mm drift tube. The lens system, being identical to the PHOIBOS 225, fits into a DN150CF flange.
SPECIFICATIONS
| Energy Resolution | < 0.2 meV (theoretical, 100 ps time resolution) |
| Angular Resolution | < 0.1° |
| k-Resolution | 0.1 A-1 |
| Acceptance Angle | ±15°, ±7°, ±4° and ±3° |
| Lateral Resolution | < 35 µm |
| Smallest Acceptance Spot | N/A |
| XPS Count Rates UHV | N/A |
| Detector Channels | 800x800 (with Channel Binning) |
| Kinetic Energy Range | 0-3500 eV |
| Pass Energies | N/A |
| Energy Dispersion | time -of-flight |
| Lens Modes | Transmission Mode, Angular Resolved Mode |
| Measurement Modes | Snapshot Mode, Sweeping Mode, Fixed Energy Mode |
| Detector | 2D DLD Detector |
| Slits/Apertures | N/A |
| Energy Window | N/A |
| Electronics | HSA + for THEMIS |
| Working Pressure | 10-11 to 10-7 mbar |
| Working Distance | 53.3 mm |
| Mounting Flange | DN150CF (8" OD) |
| Magnetic Shielding | Double µ-Metal Shielding |
| Electric Isolation | > 7 keV |